Use VCE Exam Simulator to open VCE files
This Chapter covers following
This Chapter Covers following Lab Exercises to build below topology
Note: It is not mentioned in Exam syllabus the full scope of ASR. ASR is mentioned under VM Backups. Minimum you must focus on Replication Architecture of Azure VMs in Azure Cloud to Azure Cloud
In this chapter we will add ASR to the topology which is part of Backup and Site Recovery.
We will replicate VM VMAD in West US 2 region to East US 2 region using ASR. Site Recovery Mobility Service Extension will get installed on VM VMAD when replication is enabled on VMAD.
Azure Site Recovery provides Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS).
Azure Site Recovery is an Azure Managed service that orchestrates and replicates Azure VMs and on-premises physical servers and virtual machines to the Azure cloud or to a secondary datacenter.
When outages occur in your primary location, you fail over to the secondary location to keep apps and workloads available. You fail back to your primary location when it returns to normal operations.
You can replicate Azure VMs in one Azure region to another Azure region.
You can replicate on-premises VMware VMs, Hyper-V VMs, Windows and Linux physical servers to Azure cloud or to a secondary datacenter.
Azure Recovery Services contribute to your BCDR strategy. The Azure Backup service keeps your data safe and recoverable. Site Recovery replicates, fails over, and recovers workloads when failure occurs.
Replicating Azure VMs in one region to another region in Azure Cloud: You can replicate Azure VMs from one Azure region to another Azure region.
Replicating on-premises VMs and Physical servers to Azure Cloud: You can replicate on-premises VMware VMs, Hyper-V VMs, Hyper-V VMs managed by SC VMM, Windows and Linux physical servers to Azure cloud.
Replicating to Secondary Data Center: You can replicate on-premises VMware VMs, Hyper-V VMs managed by VMM, Windows and Linux physical servers to Secondary Data Center. Note in this case we cannot replicate Hyper-V VMs to secondary Data Center.
You can replicate Azure VMs from one Azure region to another Azure region using Azure Site Recovery. Biggest advantage of this option is that ASR is integrated in the VM dashboard.
Figure below shows Azure to Azure replication architecture.
Cache storage accounts: Before source VM changes are replicated to a target storage account, they are tracked and sent to the cache storage account in source location
Site Recovery extension Mobility service: Mobility Service captures all data writes on VM disks and transfers it to Cache Storage Account.
Target resource group: The resource group to which Source VMs are replicated.
Target virtual network: The virtual network in which replicated VMs are located after failover. A network mapping is created between source and target virtual networks, and vice versa .
Target storage accounts: Storage accounts in the target location to which the data is replicated.
Target availability sets: Availability sets in which the replicated VMs are located after failover.
The Site Recovery Mobility service extension is automatically installed on the VM when you enable replication for an Azure VM.
When you initiate a failover, the VMs are created in the target resource group, target virtual network, target subnet, and in the target availability set. During a failover, you can use any recovery point.
In this exercise we will enable DR for VMAD in West US 2 Location to East US 2. Azure VM VMAD was created in Exercise 32, Chapter 2.
In Azure Portal go to VM VMAD dashboard>click Disaster Recovery in left pane> Configure Disaster Recovery blade opens>For Target Region select region as per your requirement. Here I selected East US 2.
Click Next: Advanced settings> Here you can either select system created Resource Group and Virtual Network or Select Pre Created RG and VNET. I selected System Created Resource Group and Virtual Network> I selected System Created Cache Storage Account >In Replication Settings I selected Recovery Service Vault RSVCloud. RSVCloud was created in Exercise 76, Chapter 7> Select default values for Extension settings.
Click Next: Review + Start replication. Review the settings and click Start Replication. Deployment starts in the target region. First System created resources are created in target region and then replication starts for VMAD to target region.
Go to Recovery Services Vault dashboard and click replicated items. You can see Replication status as protected. I did this step after 45 minutes.
Go to System Created Resource Group RGOnPrem-asr Dashboard. You can see VMAD OS disk and System created Virtual Network in East US 2 location.
To Failover single VM or Multiple VMs individually you can go to Replicated Items in Recovery Services Vault dashboard.
To Failover Multiple VMs together you need create Recovery Plans where you can specify order of failover. You can Create Recovery Plans in Recovery Services Vault Dashboard by clicking Recovery Plans in left pane.
In Recovery Services Vault RSVCloud click Replicated Items in left pane.
In Right pane click Item VMAD>Replicated Item Dashboard opens> From here you can failover VM or Test Failover.
Note: Disable the replication after the above exercise.
Replicate VMs located on-premises VMware hosts managed by vCenter to Azure Storage. vCenter is not compulsory but it is recommended.
VMware Virtual Machines replicate in accordance with the replication policy configured. Initial copy of the VM data is replicated to Azure Storage.
After initial replication finishes, replication of delta changes to Azure Storage begins.
VMware Machines send replication data to the process server using the Mobility service agent running on the VM.
The process server receives data from source machines, optimizes and encrypts it, and sends it to Azure Storage.
The configuration server orchestrates replication management with Azure
After replication is set up and you can run a disaster recovery drill (test failover) to check that everything's working as expected.
You can Replicate VMs located on-premises Hyper-V hosts managed by System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SC VMM) to Azure Storage. You can replicate Hyper-V VMs running any guest operating system supported by Hyper-V and Azure.
Figure below shows the Replication Architecture of Hyper-V VMs Managed by System Center VMM.
Virtual Machines replicate in accordance with the replication policy configured. Initial copy of the VM Hard disk is replicated to Azure Storage.
After initial replication finishes, replication of delta changes in VM to Azure Storage begins.
You can run a planned or unplanned failover from on-premises Hyper-V VMs to Azure. If you run a planned failover, then source VMs are shut down to ensure no data loss. Run an unplanned failover if your primary site isn't accessible.
You can Replicate VMs located on-premises Hyper-V hosts to Azure Storage. You can replicate Hyper-V VMs running any guest operating system supported by Hyper-V and Azure.
Figure below shows the Replication Architecture of Hyper-V VMs to Azure Cloud.
Requirements on Azure Side
Requirements on-premises side
Virtual Machines replicate in accordance with the replication policy configured. Initial copy of the VM Hard disk is replicated to Azure Storage.
After initial replication finishes, replication of delta changes in VM to Azure Storage begins.
You can run a planned or unplanned failover from on-premises Hyper-V VMs to Azure. If you run a planned failover, then source VMs are shut down to ensure no data loss. Run an unplanned failover if your primary site isn't accessible.
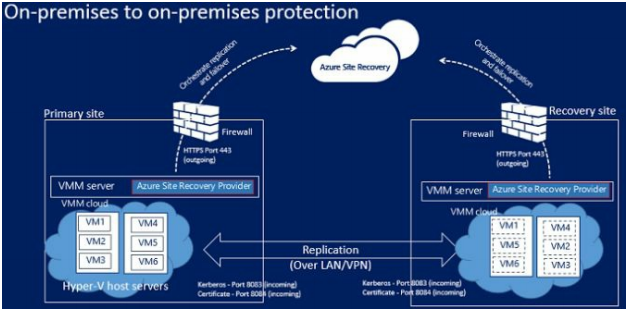
You can Replicate VMs located on-premises Hyper-V hosts managed by System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SC VMM) to secondary data center.
Figure below shows the Replication Architecture of Hyper-V VMs managed by VMM to Secondary Data Center.
VMM Server: You need VMM server in both primary and secondary location.
Hyper-V host: You need one or more Hyper-V host server (Windows Server 2016 or 2012 R2) in both primary and secondary Datacenter. Azure Site Recovery Provider will be installed on Hyper-V host.
Azure Site Recovery Provider (Installed on VMM Server): The Provider coordinates and orchestrates replication with the Site Recovery service over the internet.
Azure Site Recovery is billed based on number of instances protected.
If you are replicating VMs to Azure, then you also will be charged for consumed storage and storage transactions.
If a failover occurred and protected VMs in Azure become active, then you also will be charged for consumed Compute resources.

Top Training Courses











LIMITED OFFER: GET 30% Discount
This is ONE TIME OFFER

A confirmation link will be sent to this email address to verify your login. *We value your privacy. We will not rent or sell your email address.
Download Free Demo of VCE Exam Simulator
Experience Avanset VCE Exam Simulator for yourself.
Simply submit your e-mail address below to get started with our interactive software demo of your free trial.